Misconfigured Kubernetes Targeted by Extensive Crypto-Mining Campaign

Summary
A large-scale cryptocurrency mining campaign called RBAC Buster has been discovered actively targeting at least 60 Kubernetes clusters in the wild. The campaign exploits Kubernetes Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to create backdoors and run miners. The attackers used a misconfigured API server to gain initial access to the clusters, then deployed DaemonSets to create backdoors and run cryptocurrency miners. The campaign was discovered by cybersecurity firm Aqua Security, which had set up Kubernetes honeypots and exposed Amazon Web Services (AWS) access keys in various locations on the cluster.
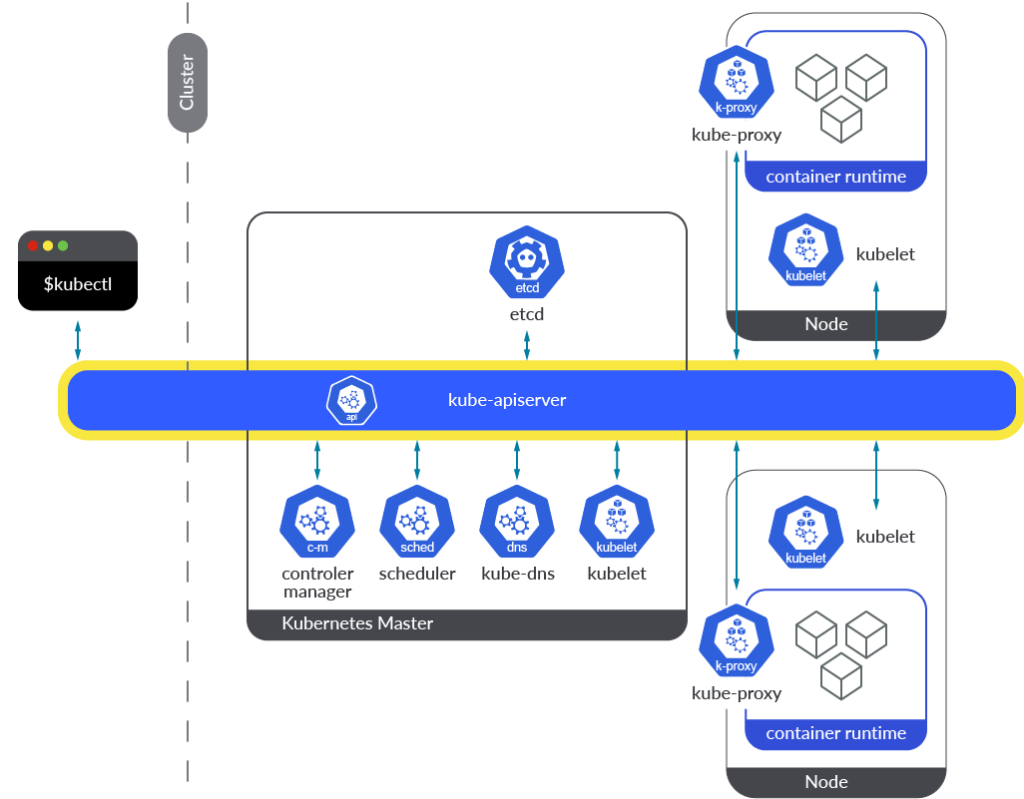
What is Kubernetes?
Kubernetes, is a widely used open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications across multiple hosts. It was developed by Google and is now overseen by the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). It provides a platform for automating the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications, making it easier to manage large, complex container environments. It also provides advanced security features and monitoring capabilities. Kubernetes is a key tool in the development of cloud-native applications and is used by many organizations to improve organizational efficiency, reduce costs, and improve security.
This widely used open-source container management tool has become a popular target for cybercriminals seeking to gain unauthorized access to organizational data for extortion or theft. The emergence of the Siloscape malware in 2021 has heightened concerns around the security of poorly configured Kubernetes clusters, leading to a Kubernetes security audit conducted by the National Computing Centre (NCC) Group.
NCC Group Audit Results
The audit identified 19 issues, with 13 in the kube-apiserver and four across Kubernetes’ broader architectural design. It highlighted concerns related to user and network permissions, as well as inadequate logging capabilities. Of the 19 issues, six were medium risk and nine were low risk, with none being critical or high. The audit also found that a “number of findings from the previous audit performed against Kubernetes version 1.13 in 2019 remain open or unfixed.”
The audit emphasized the importance of implementing robust security measures and addressing concerns related to Kubernetes’ architecture. It stressed the need to implement a mechanism for an authorization mode to subquery other authorization modes and urged the project to consider embedding authentication metadata to authorization modes. The audit also identified issues related to Kubernetes’ authorization model, which does not support “deny” rules and called for the implementation of a new “DecisionDeny” rule.
Conclusion
To secure Kubernetes environments, organizations need customizable identity and access management (IAM) solutions that specify roles and permissions for each user. Authorization levels should be specified based on the type of user, and access rules for different types of users should be established. IAM should be used to authenticate individuals, and native Kubernetes role-based access controls (RBACs) for management may need to be adjusted.
Organizations should grant the least level of privilege necessary when creating roles for each group of users and delete roles once they are no longer necessary. IAM solutions can ease the process of configuring, managing, and ensuring scalability of clusters, while correctly assigned roles will always provide a crucial layer of protection. As Kubernetes and its uses advance, security methods will evolve, but specified roles will remain an important aspect of its security.
References:
RESOURCE CATEGORIES
- Buyer's Guides(1)
- Consumer Education(39)
- Consumer Stories(2)
- Cybersecurity Consulting(4)
- Data Breaches(15)
- Data Privacy(43)
- Incident Response(2)
- Interview(51)
- MDR Services(59)
- MobileSOC(6)
- News(5)
- Press Release(101)
- Research Report(9)
- Security Assessments(2)
- Thought Leadership(19)
- Threat Hunting(3)
- Video(1)
- Vulnerability Disclosure(1)
