Domino Malware Gains Traction with Multiple Threat Actors

Summary: What is Domino Malware?
Domino (a.k.a. Minodo) is a new malware family that consists of two components, the Domino Backdoor and Domino Loader, which was first discovered in use in the fall of 2022. The Domino Backdoor collects system information, such as running processes, usernames, and computer names, and then proceeds to send this information to the attacker’s command-and-control server. Once contact is made with the command-and-control server, the threat actor sends commands to install Domino Loader. The Domino Loader is being used to deliver the final payload of an information-stealer called Project Nemesis. It is assessed that Project Nemesis is being used by ex-Conti hackers to collect data from a range of web browsers, and applications including Steam, Telegram, Discord, cryptowallets, and virtual private network (VPN) providers.
Domino Malware Background
Domino malware is assessed to be based on the Lizar post-exploitation toolkit (a.k.a. Diceloader or Tirion) due to similar coding styles and functionality, similar configuration structures, and use of the same formats for bot identification. As Lizar malware was created by the group FIN7, researchers believe that Domino malware was also created by FIN7 to spread information stealers or Cobalt Strike. Originally, the malware was observed in the wild by FIN7 in October 2022; however, by February 2023, ex-Conti hackers were reported using Domino malware to spread Project Nemesis and Cobalt Strike. It is known that FIN7 is a financially motivated threat actor group, making it highly likely that the threat actors sold access to Domino malware to ex-Conti hackers to increase the group’s profits.
Domino Malware Attack Pattern
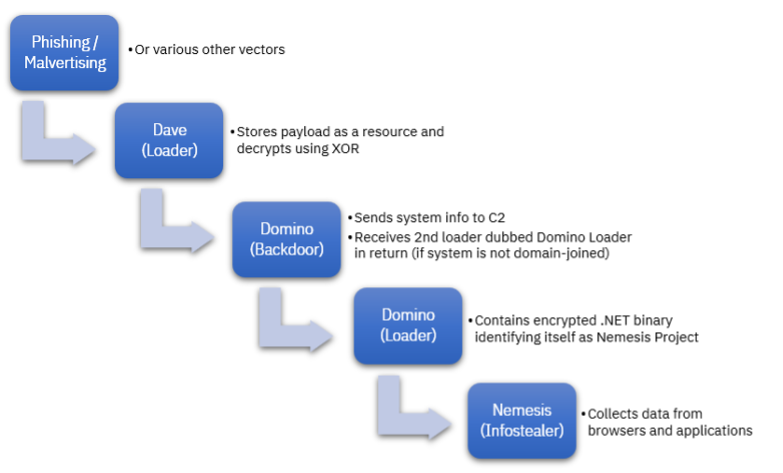
There are two potential methods for the malware to gain initial access. The first method relies on phishing or malvertising attacks, while the second exploits Domain Name System (DNS) security gaps to breach corporate systems. Once a victim clicks on a suspicious link, a loader called “Dave” is used to drop the Domino Backdoor. The Domino backdoor then begins to collect basic system information to send to an external command-and-control server. The command-and-control server then returns an Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encrypted payload to the compromised system, with the payload being the Domino Loader. The Domino Loader contains an encrypted .NET binary that can contain either Project Nemesis or Cobalt Strike, enabling the threat actors to maintain persistence on the victim’s system.
Targeted Technology
Windows Endpoint OS
Conclusion
Domino malware is still relatively new and while it currently only drops Cobalt Strike or Project Nemesis, it is possible that the malware will be updated to drop other malware developed by FIN7 in the future. It is highly likely that FIN7 will continue to package their developed malware to sell to other organizations to increase the group’s profits. Collaboration between different cyber threat groups highlights the complex and ever-changing nature of the cybercrime economy. Organizations must remain vigilant and adopt robust security measures, including predictive DNS technology, to mitigate the risk of being targeted by sophisticated cyber-attacks.
The Critical Start Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) team will continue to monitor the situation and work closely with the Threat Detection Engineering (TDE) team and the SOC to implement any relevant detections. For future updates, the CTI team will post via ZTAP® Bulletins and on the Critical Start Intelligence Hub.
References:
RESOURCE CATEGORIES
- Buyer's Guides(1)
- Consumer Education(39)
- Consumer Stories(2)
- Cybersecurity Consulting(4)
- Data Breaches(15)
- Data Privacy(43)
- Incident Response(2)
- Interview(51)
- MDR Services(59)
- MobileSOC(6)
- News(5)
- Press Release(101)
- Research Report(9)
- Security Assessments(2)
- Thought Leadership(19)
- Threat Hunting(3)
- Video(1)
- Vulnerability Disclosure(1)
